In today's digital age, the web browser has become an essential tool for almost everyone. Whether you're browsing the internet for information, shopping online, or connecting with friends and family, a web browser is the gateway to the vast world of the internet. But have you ever wondered what exactly a web browser is and how it works? Understanding the basics of web browsers can enhance your online experience and help you make informed decisions about the tools you use daily.
As technology continues to evolve, the role of web browsers has expanded beyond simply displaying web pages. They now serve as powerful platforms for running applications, streaming media, and managing sensitive data. In this article, we will delve into the fundamental aspects of web browsers, exploring their functions, types, and how they impact your online life.
By mastering the basics of web browsers, you can optimize your internet usage and ensure a safer, more efficient browsing experience. Whether you're a casual user or a tech enthusiast, understanding the inner workings of this critical tool is invaluable.
Read also:Bloodhound Lil Jeff Killed Video Uncovering The Truth Behind The Tragic Story
Table of Contents
- What Is a Web Browser?
- History of Web Browsers
- How Web Browsers Work
- Types of Web Browsers
- Key Components of Web Browsers
- Popular Web Browsers
- Browser Security and Privacy
- Web Browser Compatibility
- Choosing the Right Web Browser
- Future of Web Browsers
What Is a Web Browser?
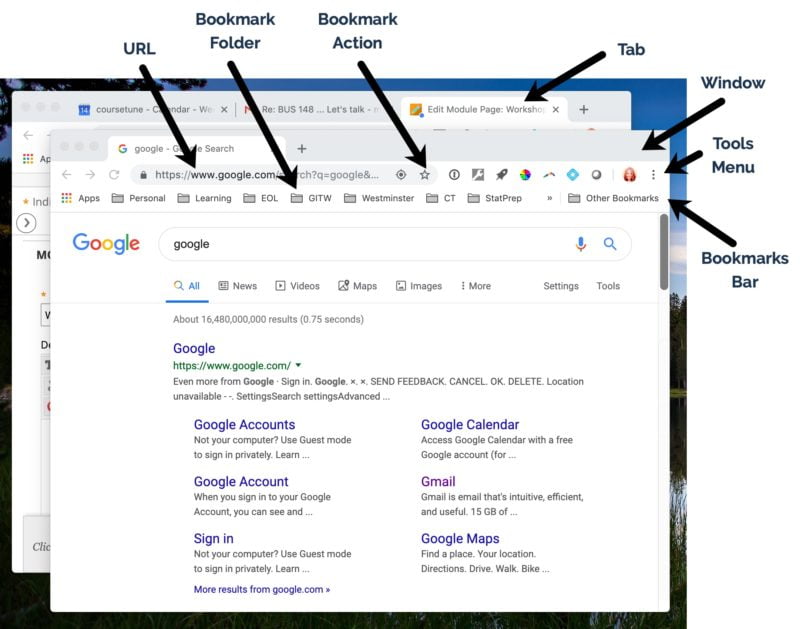
A web browser, often referred to simply as a "browser," is a software application that allows users to access and interact with content on the World Wide Web. It retrieves, presents, and traverses information resources identified by URLs (Uniform Resource Locators). These resources can include web pages, images, videos, and other types of content.
Web browsers act as intermediaries between users and the internet, interpreting HTML (HyperText Markup Language), CSS (Cascading Style Sheets), and JavaScript to render web pages in a visually appealing and functional manner. Understanding what a web browser is and how it operates is crucial for anyone who uses the internet regularly.
Importance of Web Browsers
- Facilitates access to information and services online.
- Enables interaction with websites and applications.
- Provides tools for enhanced productivity and entertainment.
History of Web Browsers
The concept of web browsers dates back to the early days of the World Wide Web. The first web browser, named "WorldWideWeb," was created by Sir Tim Berners-Lee in 1990. This browser was later renamed "Nexus" and laid the foundation for modern browsing technology.
Since then, numerous browsers have emerged, each introducing new features and improvements. The evolution of web browsers has been marked by significant milestones, including the launch of Mosaic in 1993, Netscape Navigator in 1994, and Internet Explorer in 1995. Today, browsers like Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Safari dominate the market.
Key Milestones in Web Browser Evolution
- 1990: Creation of the first web browser by Tim Berners-Lee.
- 1993: Release of Mosaic, the first widely used web browser.
- 2003: Introduction of Firefox, known for its open-source nature.
How Web Browsers Work
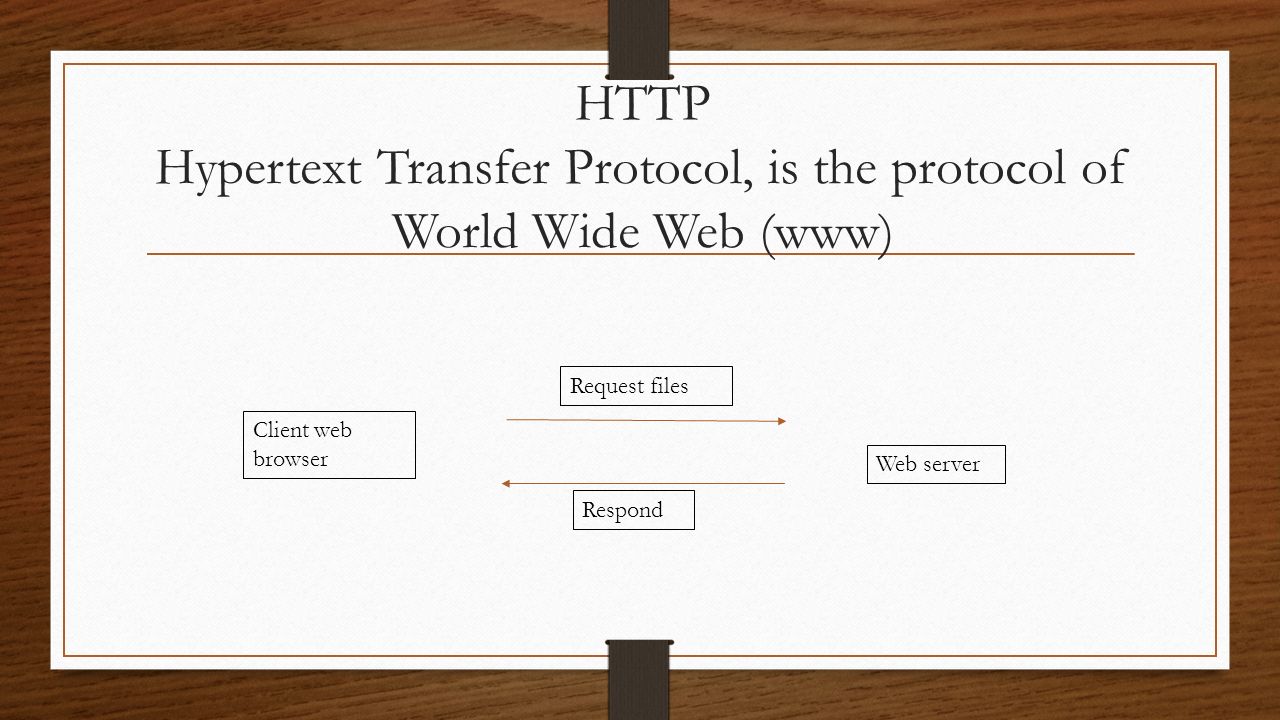
Web browsers function by sending requests to server computers that host web content. When you enter a URL or click a link, the browser communicates with the server to retrieve the requested data. This data is then processed and displayed on your screen.
Behind the scenes, web browsers perform several critical tasks, including:
Read also:Movierulz Today 2024 The Ultimate Guide To Downloading Movies Safely And Legally
- Parsing HTML, CSS, and JavaScript code.
- Rendering web pages by applying styles and layouts.
- Managing interactions such as clicks, form submissions, and media playback.
This process happens almost instantaneously, providing users with seamless access to web content.
Types of Web Browsers
There are various types of web browsers available today, each catering to different user needs and preferences. The most common categories include:
Desktop Browsers
Designed for use on computers and laptops, desktop browsers offer advanced features and customization options. Examples include Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Microsoft Edge.
Mobile Browsers
Tailored for smartphones and tablets, mobile browsers prioritize speed and efficiency. Popular choices include Safari for iOS and Chrome for Android.
Specialized Browsers
These browsers target specific audiences or use cases, such as privacy-focused browsers like Tor or lightweight browsers for older devices.
Key Components of Web Browsers
A web browser is composed of several integral components that work together to deliver a smooth browsing experience. These components include:
- Rendering Engine: Responsible for processing HTML, CSS, and images to display web pages.
- JavaScript Interpreter: Executes JavaScript code to enable dynamic interactions.
- Networking Layer: Handles communication with web servers and manages data transfer.
- User Interface: Includes elements like the address bar, bookmarks, and tabs for easy navigation.
Popular Web Browsers
With numerous options available, choosing the right web browser can be overwhelming. Below are some of the most popular browsers and their standout features:
Google Chrome
Known for its speed and extensive extension library, Google Chrome is the world's leading browser. It integrates seamlessly with Google services and offers robust security features.
Mozilla Firefox
Firefox is celebrated for its open-source nature and commitment to user privacy. It also supports a wide range of add-ons for enhanced functionality.
Apple Safari
Designed specifically for Apple devices, Safari emphasizes energy efficiency and fast performance. It is optimized for macOS and iOS users.
Browser Security and Privacy
As web browsers handle sensitive information, ensuring security and privacy is paramount. Modern browsers employ various techniques to protect users, such as:
- HTTPS encryption to secure data transmission.
- Phishing and malware protection to prevent access to harmful sites.
- Private browsing modes to limit data tracking and storage.
Users should also adopt best practices, such as keeping browsers updated and using strong passwords, to enhance their online safety.
Web Browser Compatibility
Compatibility refers to a browser's ability to correctly display and interact with web content. While standards like HTML5 and CSS3 aim to ensure consistency across browsers, differences in implementation can lead to compatibility issues. Developers often test their websites on multiple browsers to ensure a uniform user experience.
Tools like cross-browser testing platforms and polyfills can help address compatibility challenges, ensuring that web applications function as intended on all major browsers.
Choosing the Right Web Browser
Selecting the best web browser depends on individual preferences and requirements. Factors to consider include:
- Performance: Speed and resource consumption.
- Privacy: Data protection and tracking policies.
- Features: Availability of extensions, themes, and other customizations.
By evaluating these aspects, users can find a browser that aligns with their needs and enhances their browsing experience.
Future of Web Browsers
The future of web browsers looks promising, with ongoing advancements in technology driving innovation. Key trends include:
- Improved artificial intelligence integration for enhanced user assistance.
- Greater emphasis on privacy and security features.
- Development of lightweight browsers for emerging markets and low-end devices.
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, web browsers will remain at the forefront of enabling seamless and secure internet access.
Conclusion
In conclusion, mastering the basics of what a web browser is and how it operates is essential for anyone navigating the digital world. From understanding its history and components to exploring popular options and future trends, this knowledge empowers users to make informed decisions about their browsing tools.
We encourage you to share your thoughts and experiences in the comments below. Additionally, feel free to explore other articles on our site for more insights into technology and digital lifestyle topics. Together, let's continue learning and growing in our digital journey.
Data and information in this article are sourced from reputable publications such as Mozilla, Google Chrome, and W3C, ensuring accuracy and reliability.